You are in: Europe
Change location
You are here
Tools for finding reviewers and how to use them
Tools for finding reviewers and how to use them
The following sites and tools can be use to identify suitable reviewers from outside the Sage Track system:
- Web of Science
- PubMed
- Scopus
- JANE tool
- Search engine
- Web of Science Reviewer Recognition
- Google Scholar
- Reference list
Web of Science
The Web of Science Core Collection is a database for papers published in indexed journals. The collection of citation indexes represents the citation connections between scholarly research articles found in the most globally significant journals, books, and proceedings in the sciences, social sciences and art & humanities.
NOTE To access all the content and features, you need a Web of Science Core Collection subscription. If you are not affiliated to one of the institutions listed in the homepage, you cannot create an account.
Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
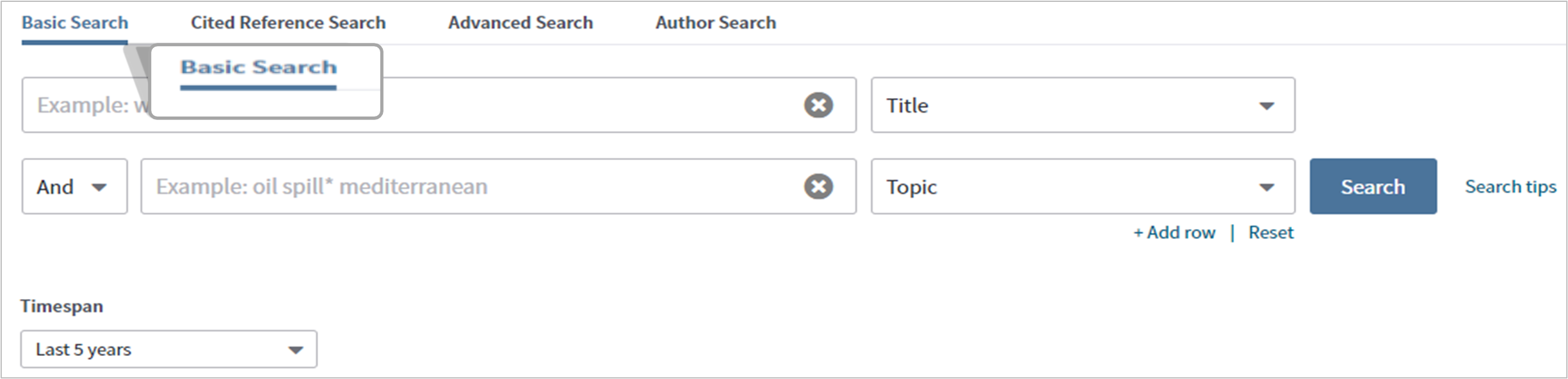
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button.
TIP Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips.
Results page
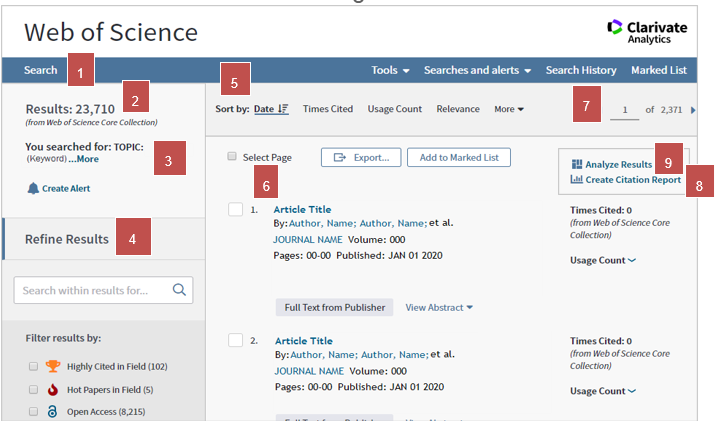
- New Search
- The number of results from the search
- List of keywords selected for the search
- Refining results tools
- Area to reorder results
- Article results
- Change to another page of results
- Analyze Results tool
- Times Cited
Viewing an article
To view an article, select the title from the Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button.
TIP Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips.
Result Page:

Article information will appear when the page reloads. This will include the full list of authors, journal information, keywords, the abstract and the email address of the corresponding author.
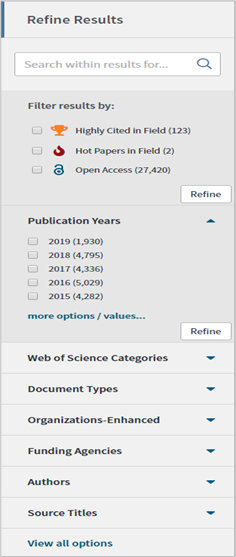
Refine search
Select a subsection by clicking the blue triangle
- Select one or more of the checkboxes and select ‘Refine’
- Multiple checks in different subsections are allowed
- For more advanced refining, select ‘more options / values…’
- Check the boxes the search should include or exclude
- Select ‘Refine’ or ‘Exclude’
- Using the exclude function can help ensure the institutions or authors associated with the manuscript are not included in the results.
Modify the time span
- In some cases, extending or reducing the time span of a search will provide more reviewers in that area of study and / or reviewers that are more responsive
- Begin a new search
- Select the ‘Timespan’ dropdown menu and select a different timespan.
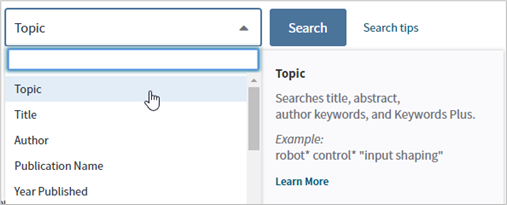
KeyWords Plus
- After finding an article that encapsulates the topic(s) of the manuscript, view the manuscript and scroll to ‘KeyWords Plus’ (underneath ‘Author Keywords’)
- The keywords listed may offer new keywords to use in another search
- Selecting one of the keywords will direct you to a new search that does not include your previous search.

Sort by
Sort by times cited
- Sorting the search results by how many times an article has been cited may indicate the expertise of the authors in their field
- On the Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button
TIP Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips.
- Results page, sort by ‘Times Cited’
- The number of times an article has been cited can be found on the right side of an article.
Sort by source titles
- Refining the results to ‘Source Titles’ will limit results to journals that publish similar research to the manuscript’s topic
- While in the Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button
TIP Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips.
- Results page, locate the ‘Refine Results’ section
- Select the ‘Source Title’ section
OR
- While in the Analyze Results tool, locate the categories on the left
- Select the ‘Source Title’ category.
View cited references
- After finding an article that encapsulates the topic(s) of the manuscript, scroll to the bottom to view all the cited references
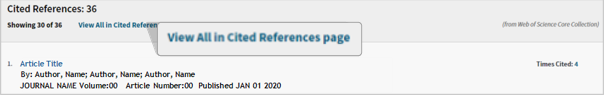
- Select the blue title to view the article
- If the title is not in blue, it cannot be selected.
TIPS
- Create a new window or tab to view the article since it is not possible to return to the previous search
- Be aware of who is in the author list and when a cited paper was published
PubMed
PubMed comprises more than 30 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full-text content from PubMed Central and publisher websites.
Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript and determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the PubMed homepage, make sure ‘PubMed’ is selected from the drop-down menu next to the search field

- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword(s) in the search bar (suggestions will display as you type your keywords) and select search
- Detailed instructions on using the basic search feature can be found here
- More refined searches can help to narrow the results list to best fit your manuscript:
- Keyword search in title only: KEYWORD[TITLE]
- Keyword search in title and abstract: KEYWORD[TITLE/ABSTRACT]
- To string keywords together, you can use ‘AND’, ‘OR’, ‘NOT’ between them to include or exclude keywords from your search
- For a full list of fields that you can use to refine your search please refer to the drop-down menu on the Advanced Search Builder page
- Most used search functions:
- TITLE: Usually a keyword that is essential to the manuscript. For example, all manuscripts from a journal that focuses on HIV and AIDS may want articles with ‘HIV’ or ‘AIDS’ in the title;
- TITLE/ABSTRACT: A keyword or phrase that is important to the manuscript, but may not always appear in the title. For example, a specific drug name or a specific medical condition. For example, ‘children’ could be used to refine the search to only include articles about children;
- MeSH terms: A way to refine phrases that include the keyword. This is useful when the terminology of the manuscript is unfamiliar or if the results were too broad.
NOTE You can also use the Advanced Search Builder to build more complex search strings. The fields auto-populate as well. The search string you construct appears in the field at the top of the page. Video instructions can be found on YouTube.
Results page
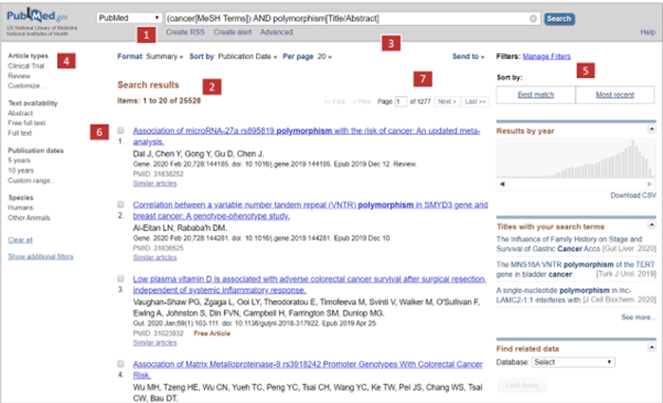
- New search
- The number of results from the search
- List of keywords selected for the search
- Refining results tools
- Area to reorder results
- Article results
- Change to another page of results
Viewing an article
To view an article, select the title from the Results page.
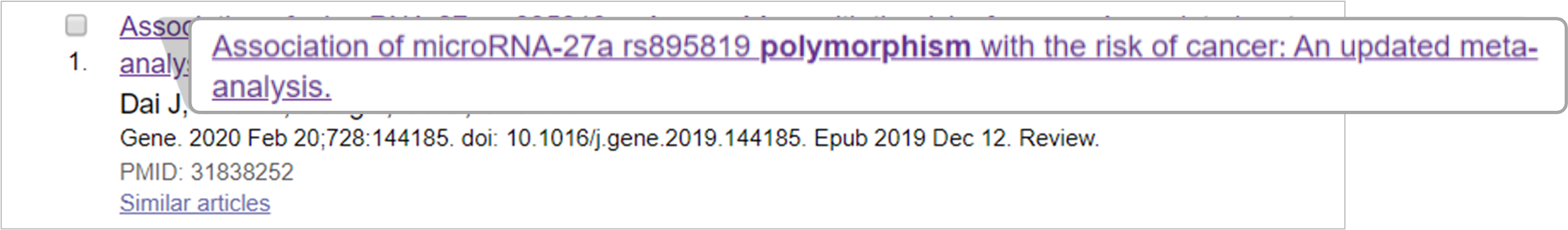
Article information will appear when the page reloads. This will include the full list of authors, journal information, keywords, the abstract and the email address of the corresponding author. It will also include similar articles and articles the paper was cited by, if applicable, which may be useful to search for additional reviewers closely related to the topic.

If the corresponding author email address does not appear in the ‘Author Information’ section, you can check the article using the Full text link (if present), at the top right.
Refine search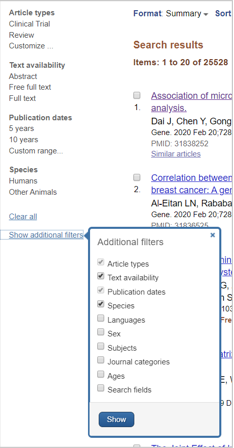
Select a field to refine by from one of the categories and a filter will be applied.
- Select additional fields and they will be automatically applied
- For additional filters, select ‘Show additional filters’, check the filter(s) you would like and select ‘Show’
- To remove a filter, select the field(s) you’ve filtered by and they will automatically be removed. Alternatively, you can clear all filters by selecting ‘Clear All’ at the top of the search results list.
Modify the time span
- In some cases, extending or reducing the time span of a search will provide more reviewers in that area of study and/or reviewers that are more responsive
- You can filter by 5 years or 10 years as well as a custom range by selecting from the filter options on the left side of the screen in the ‘Publication dates’ category.
Sort by
Sort by Most Recent or Publication Date
- Sorting the search results by date will allow you to identify the most recent researchers in the field and who may be most relevant for reviewing new research
- On the Results page sort by ‘Most Recent’ or ‘Publication Date’
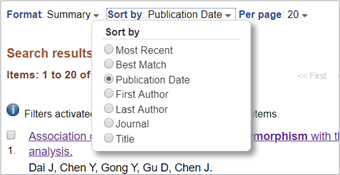
Sort by Best Match
- Sorting by ‘Best Match’ will yield articles that are the closest match to your keyword search and may reveal researchers who have the greatest expertise in the field
TIPS
- You may need to use keywords that were not provided by the author or in the title
- Using MeSH terms or gathering keywords from the manuscript can be useful
- If emails are not provided, look under ‘Full Text Link’ and select one of the links
- PMC, Springer Link, Oxford Academic, PLOS One, and Wiley Online Library are the most reliable
- When looking at an article, a section called ‘Related information’ will occasionally appear on the bottom right of the screen under ‘Similar Articles’. Here you can select ‘Articles frequently viewed together’ to view more articles that are similar to each other.
Scopus
Scopus is a source-neutral abstract and citation database curated by independent subject matter experts. It places powerful discovery and analytics tools in the hands of researchers, librarians, institutional research managers and funders.
Scopus provides a number of useful tutorials and FAQ pages that you can use to supplement this guide.
Note: Check if you have access via your institution. If not, you can create an account for free access to Scopus preview.
Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript and determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- Go to the Scopus Document search page
- Use the Basic Search to search documents, authors, or affiliations
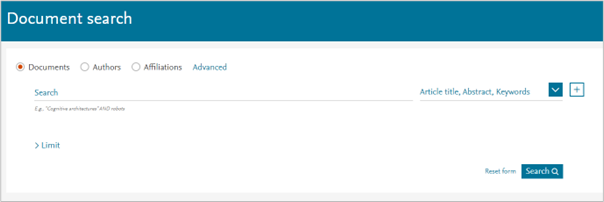
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine what field the keyword will be searched in (or select all fields) using the drop-down menu on the right
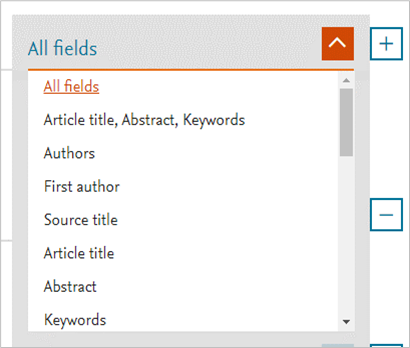
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+’. After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘And Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, adjust the fields to span the last 5 years if searching by the Published date. There is also an option to search by how recently an article was added to Scopus (within the past 7, 14, or 30 days)
- There are also filter options to search by a specific document type or all documents as well as what type of access there is to the document (All or Open Access)
- Select the ‘Search’ button.
TIP Select ‘Search tips’ to the right of the search field for additional search tips. This includes recommended practices for using Boolean and Proximity operators, searching using exact or approximate phrases, and search filters.
Advanced search
- The advanced search allows for the construction of complex query strings. Information on best practices for this feature can be found here.
Results page
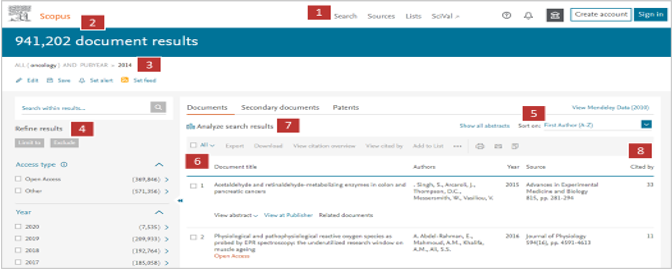
- New Search
- The number of results from the search
- List of keywords selected for the search
- Refining results tools
- Area to reorder results
- Article results
- Analyze search results tool
- Times Cited
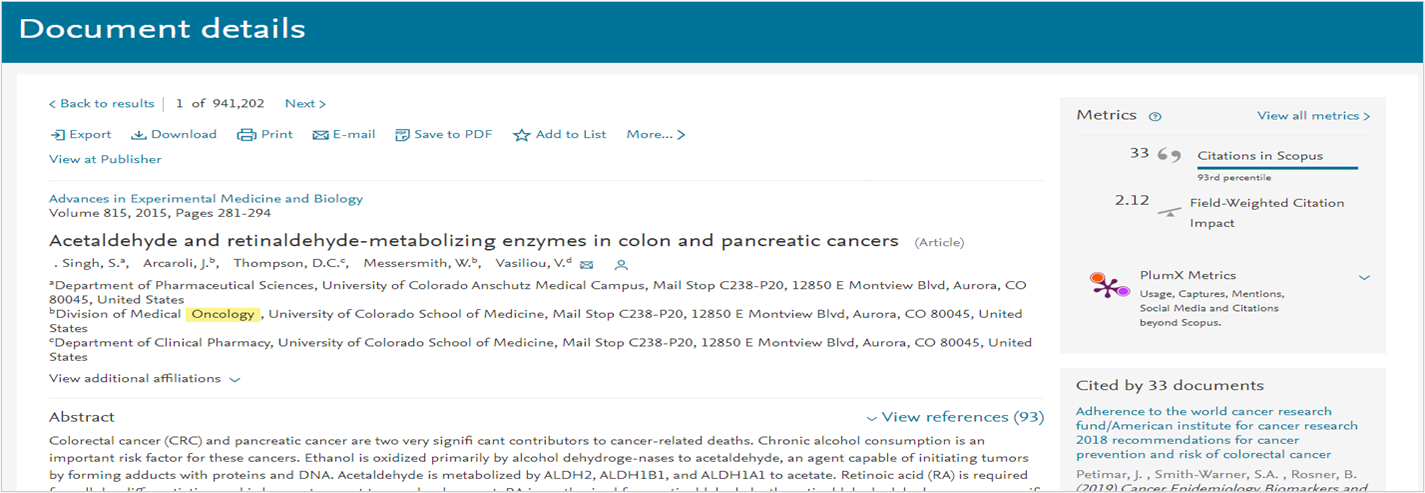
Viewing an article
To view an article, select the title from the Basic search

- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button.
TIP Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips.
Results page
Article information will appear when the page reloads. This will include the full list of authors, journal information, keywords, the abstract and the email address of the corresponding author. It will also include articles the paper was cited by, which may be useful to search for additional reviewers closely related to the topic.
Refine search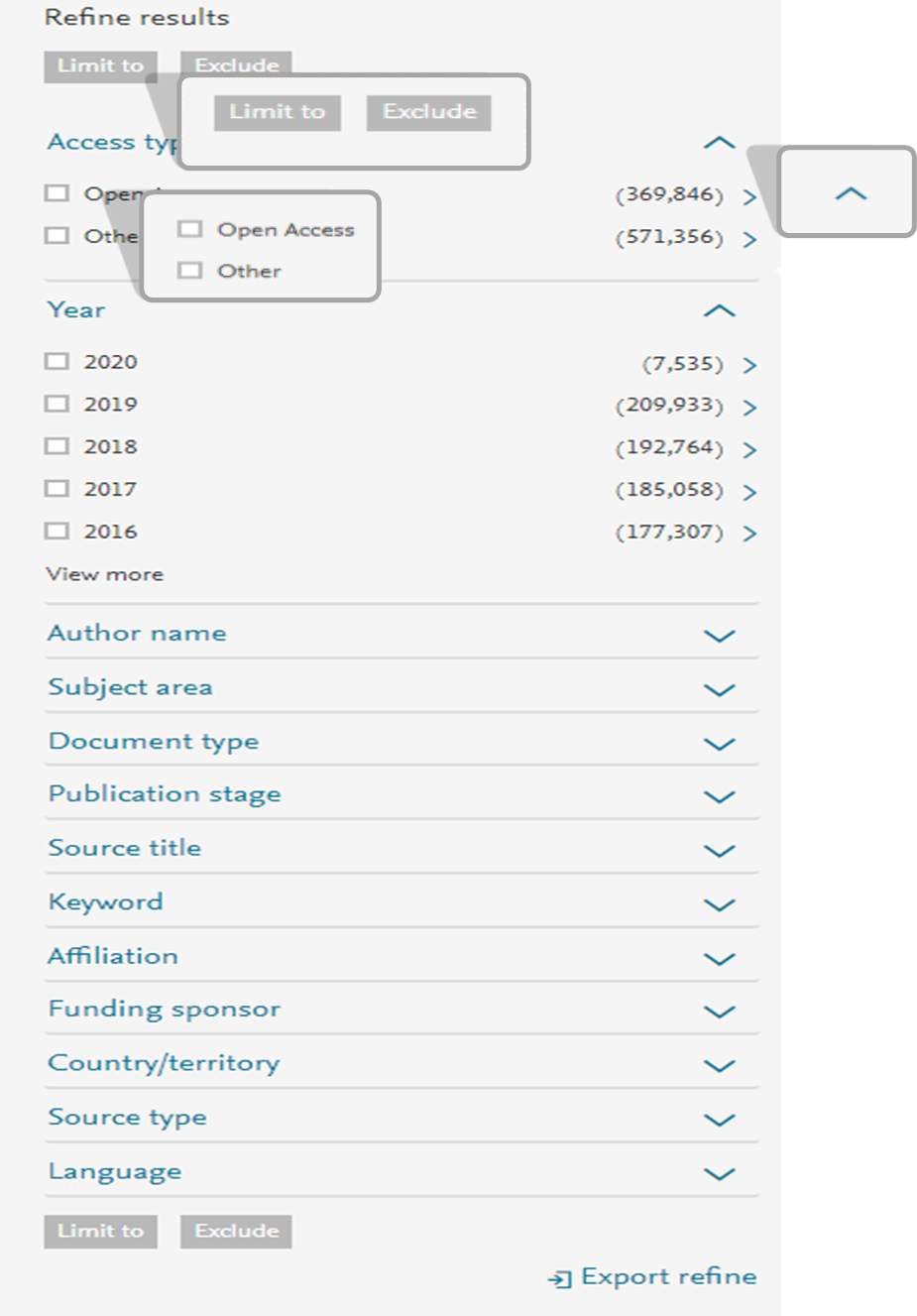
- Select a subsection by clicking the blue triangle
- Select one or more of the checkboxes and select ‘Limit to’ or ‘Exclude’
- Multiple checks in different subsections are allowed
- Using the exclude function can help ensure the institutions or authors associated with the manuscript are not includedin the results.
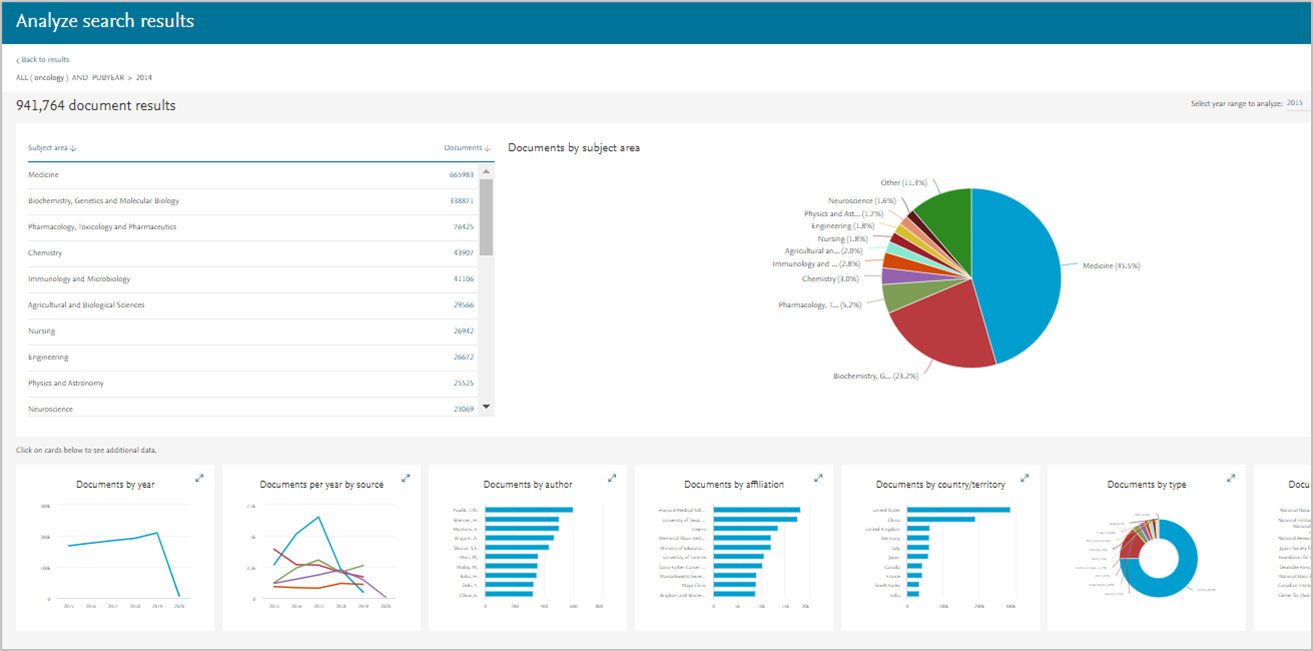
Visuals
-
To analyze the results, click the “Analyze search results”. This option will allow you to see research trends in the resulting papers.
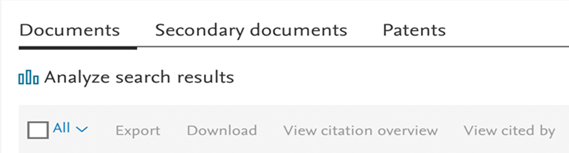
- To change the visual type, either go back one page in the browser or select a visualization from the images at the bottom of the screen
- To adjust the year range to analyze, adjust the range using the drop-down menu on the right side of the page and select ‘Analyze’
- To sort sub-categories in ascending or descending alphabetical order, select the ‘Subject area’ icon at the top of the sub-category list on the left side of the screen.
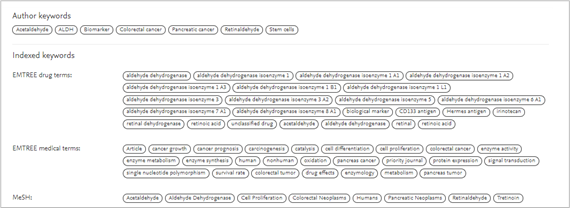
Additional keywords
- After finding an article that encapsulates the topic(s) of the manuscript, view the manuscript and scroll to the Author keywords and Indexed keywords sections
- The keywords listed may offer new keywords to use in another search.
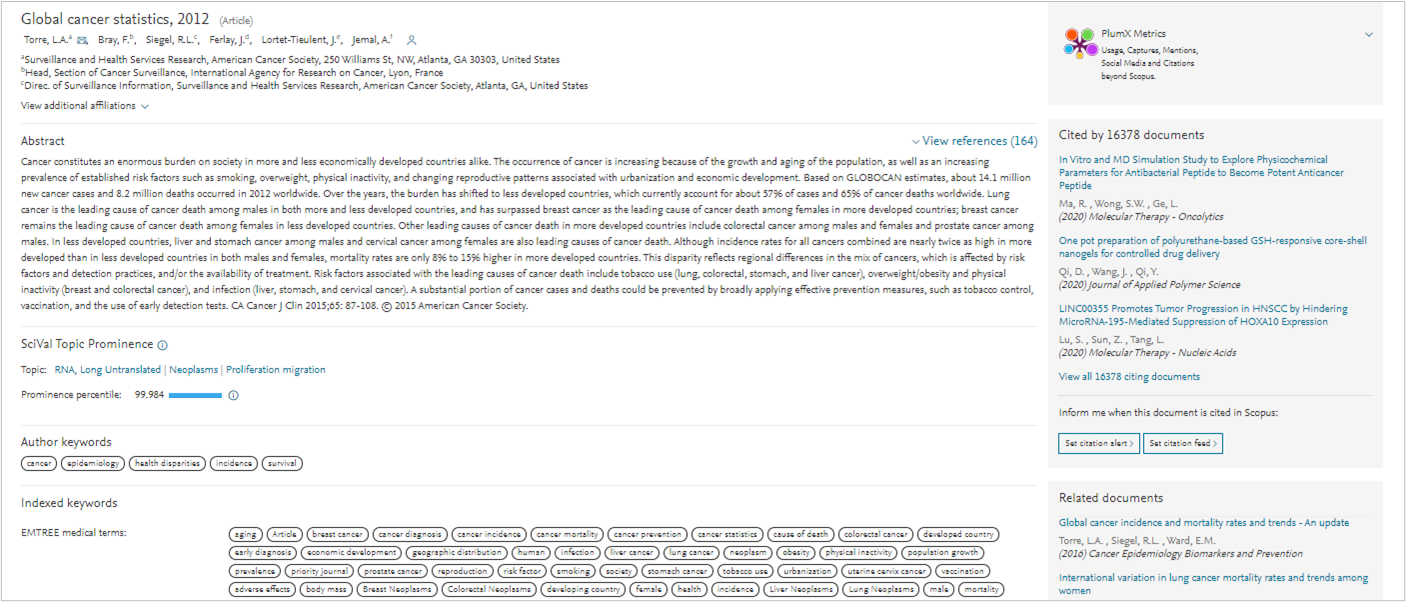
References as a source for additional authors
- At the end of a manuscript page, all articles referenced by the manuscript are listed
- This can be a useful source for finding additional relevant reviewers
- Select a manuscript and on the manuscript information page you can find corresponding author information and email addresses.
Related articles as a source for additional authors
- On the ‘document results’ page, selecting ‘Related documents’ for any manuscript will display a list of all related articles
- On a manuscript page, you can identify related documents based on the author list or author-provided keywords in a section on the right side of the screen.
Sort by
Sort by Times Cited 
- Sorting the search results by how many times an article has been cited may show the expertise of the authors in their field
- The number of times an article has been cited can be found on the right side of an article.
Sort by source titles
- Refining the results to ‘source titles’ will limit results to journals that publish similar research to the manuscript’s topic
While in the Basic search
- Read over the abstract and/or the manuscript to determine a few keywords that best encapsulate the topic(s) of the manuscript
- At the top of the Web of Science homepage, select the ‘Search’ button or the ‘Web of Science’ icon
- Use the Basic Search to search keywords
- Insert the keyword in the search bar and determine how the keyword will be searched in the drop-down menu on the right (an explanation of how the keyword will be searched will appear when the mouse hovers over a category)
- Add more keywords to the search by selecting ‘+ Add row’
- After adding another row, determine if the keywords should be included or excluded from the search by selecting ‘And’, ‘Or’ or ‘Not’
- Determine the timespan. For best results, select ‘Last 5 years’
- Select the ‘Search’ button.
TIP: Select ‘search tips’ next to the search button for additional search tips
- Results page, locate the ‘refine results’ section
- Select the ‘source title’ section.
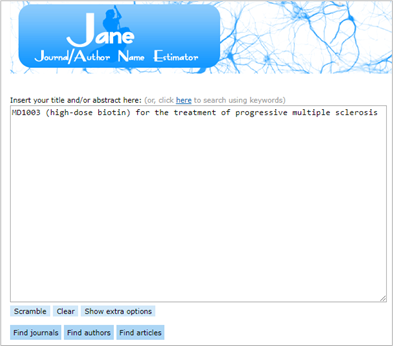
JANE tool
- Jane tool will compare your document to documents in PubMed to find similar journals, authors or articles
- Enter the title, partial title or abstract and select either ‘Find authors’ or ‘Find articles’
- There is also an option to search by keywords
- Results will display in order of relevance.
Example
- Enter the title or abstract in the space provided
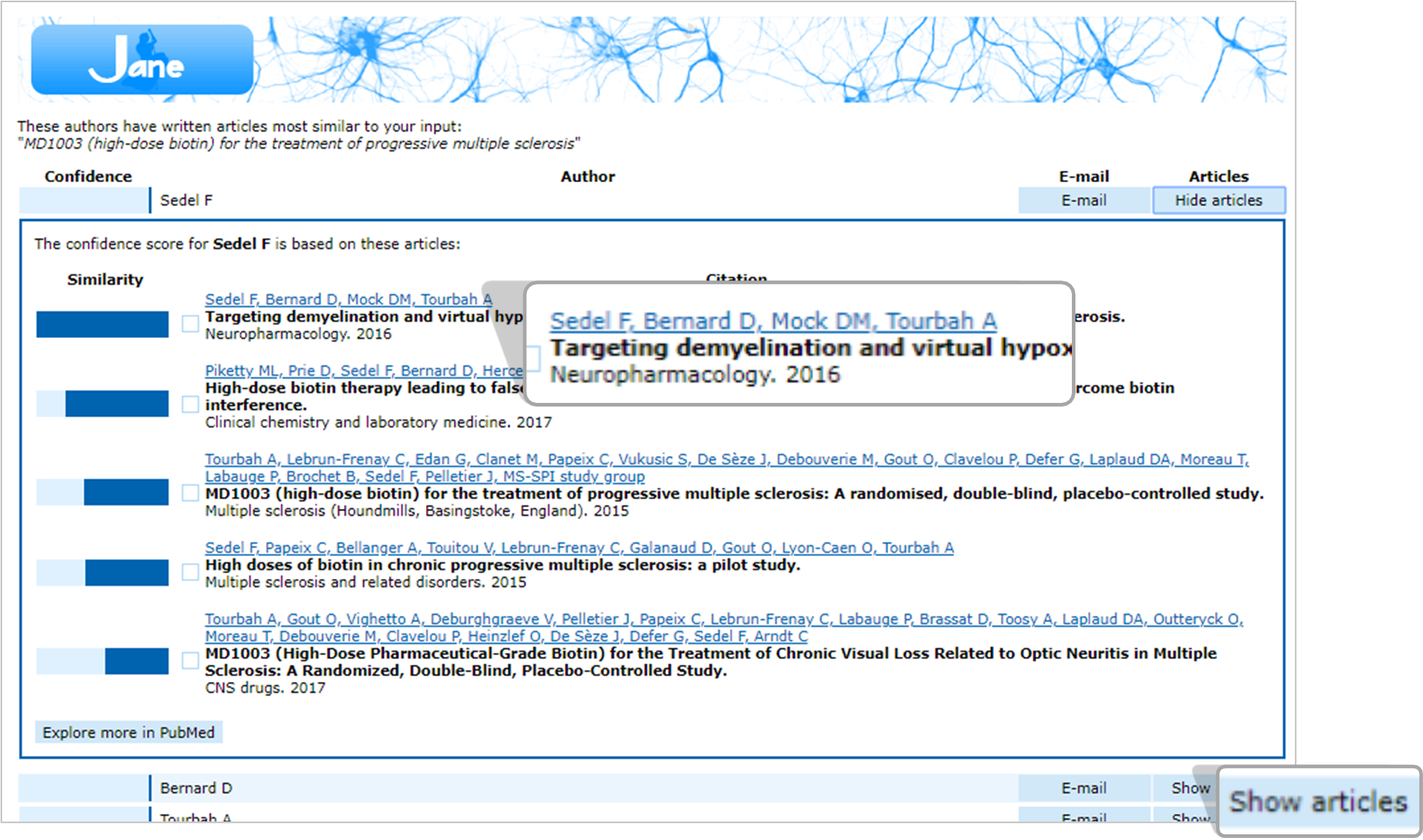
- For ‘Find authors’, click ‘Show articles’ against an author’s name
- Click on the hyperlinked name(s) to be taken to the PubMed entry
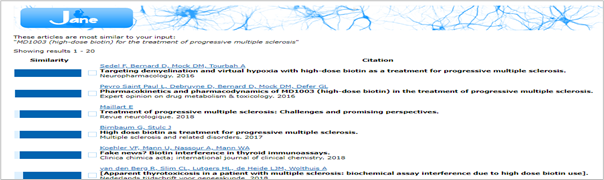
- For ‘Find articles’, click on the hyperlinked name(s) to be taken to the PubMed entry
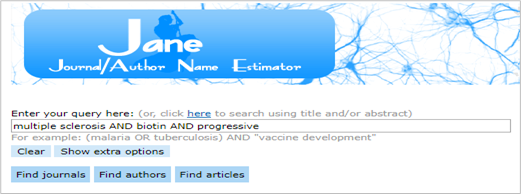
- To search by keywords, use Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) along with the key terms.
Search engine
- Search specifically for academic institutions using the ‘site:.edu’, ‘site:.ac.uk’, etc. tag after an appropriate keyword(s) e.g. turbomachinery site:.edu
- This may generate faculty pages for academics with related research interests
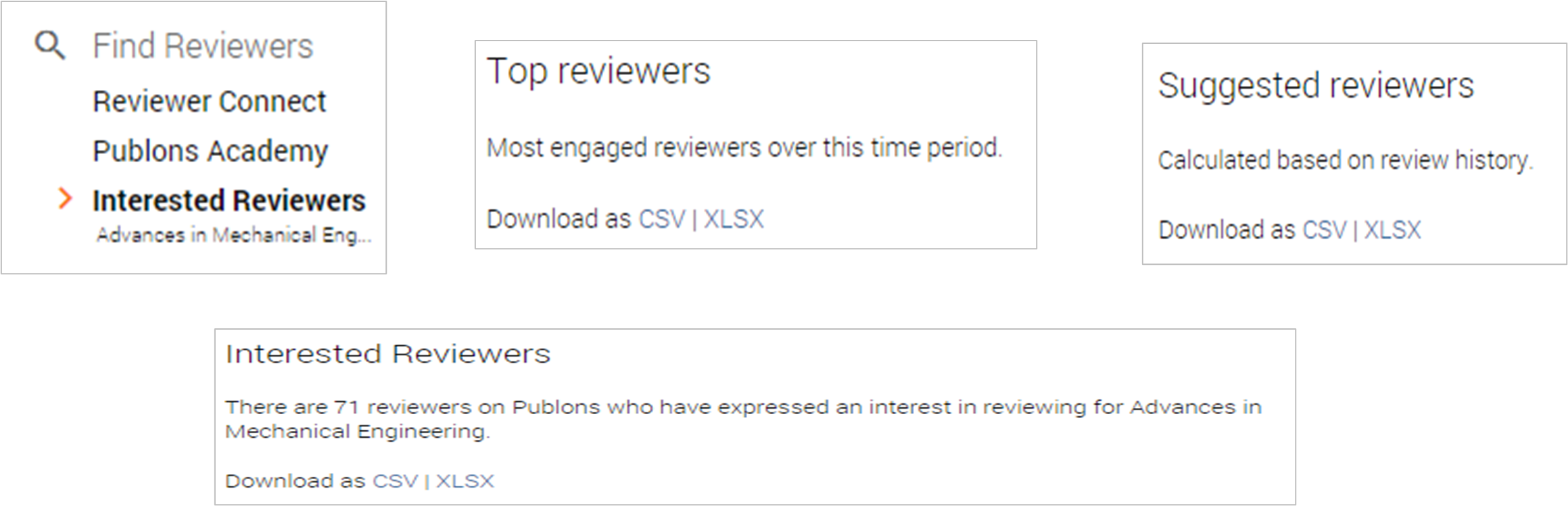
Web of Science Reviewer Recognition
Through the Sage partner dashboard, you can view lists of each journal’s top reviewers, suggested reviewers who review for similar journals, and researchers who have expressed interest in reviewing for your journals.
Use these tools to build or expand a journal’s pool of reviewers. They are not designed to find reviewers for specific papers.
Contact your Sage Publishing Editor for access to the dashboard.
Each reviewer verified by Reviewer Recognition has a reviewer profile that lists a wealth of information such as a link to their institutional webpage, a list of their verified reviews, which journals they have reviewed for, whether they sit on any editorial boards, how many articles they have published, and the number of times they have been cited.
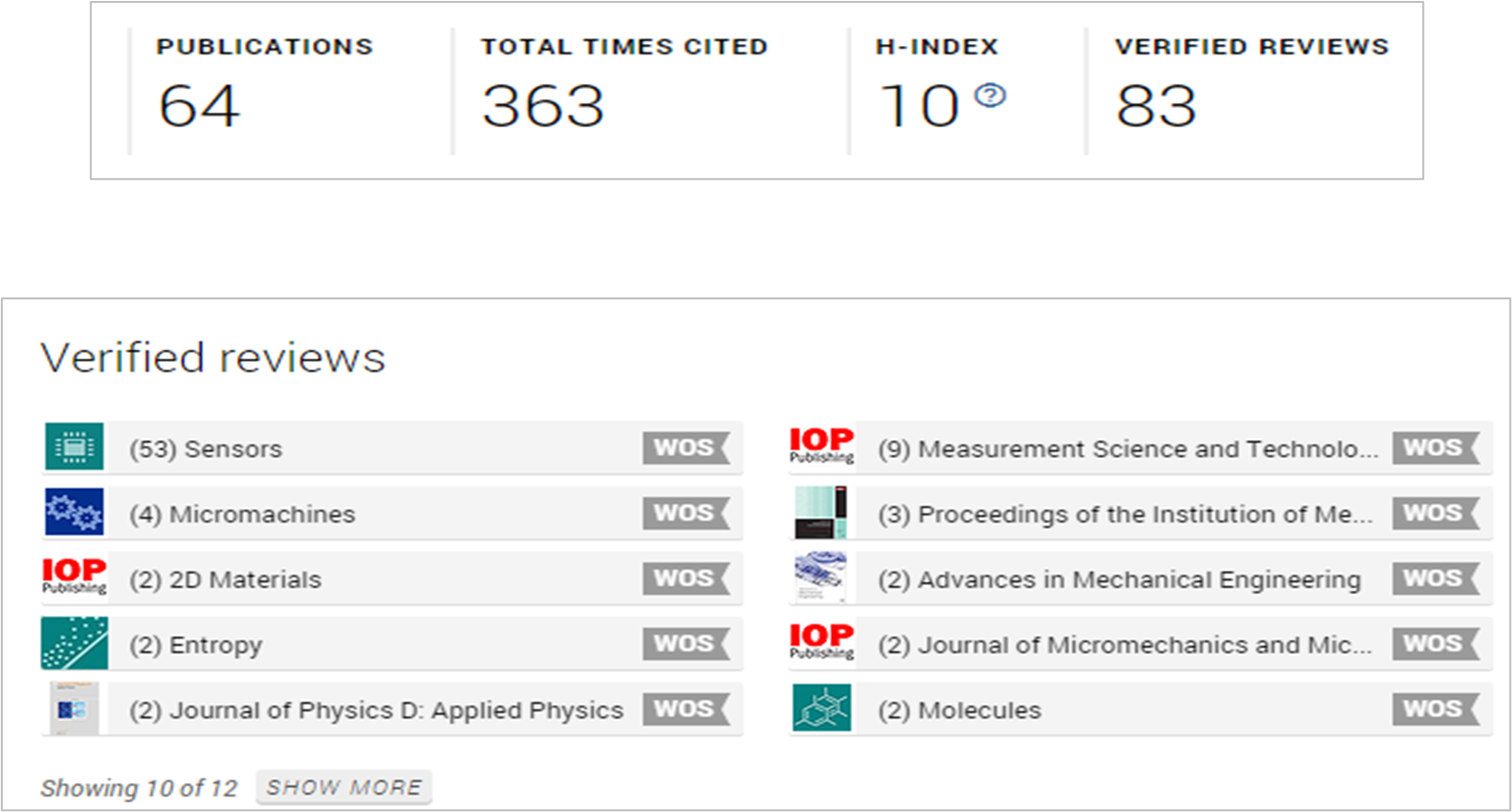
Note that you will still need to verify the identity of potential reviewers you find on Reviewer Recognition by following the steps outlined in the ‘reviewer verification’ section below.
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is a an open-access web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across a range of publication formats and disciplines: theses, books, abstracts and court opinions, from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other web sites. It is estimated that it has approximately 80-90% coverage of all articles published in English. However, be cautious, as Google Scholar does not veto journals and includes predatory journals in its index.
Basic search
Insert the keyword(s) in the search bar (suggestions will display as you type your keywords) and select search.

- Detailed instructions on using the basic search feature can be found https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/help.html#searching
- More refined searches can help to narrow the results list to best fit your manuscript:
- To string keywords together, you can use ‘AND’, ‘OR’, ‘NOT’ between them to include or exclude keywords from your search. If you want to restrict the results to certain keyword(s), enclose them in quotation marks.
- For a full list of fields that you can use to refine your search please refer to the menu on the Advanced Search option https://scholar.google.com/schhp?hl=en#d=gs_asd&t=1654015030472
Results page
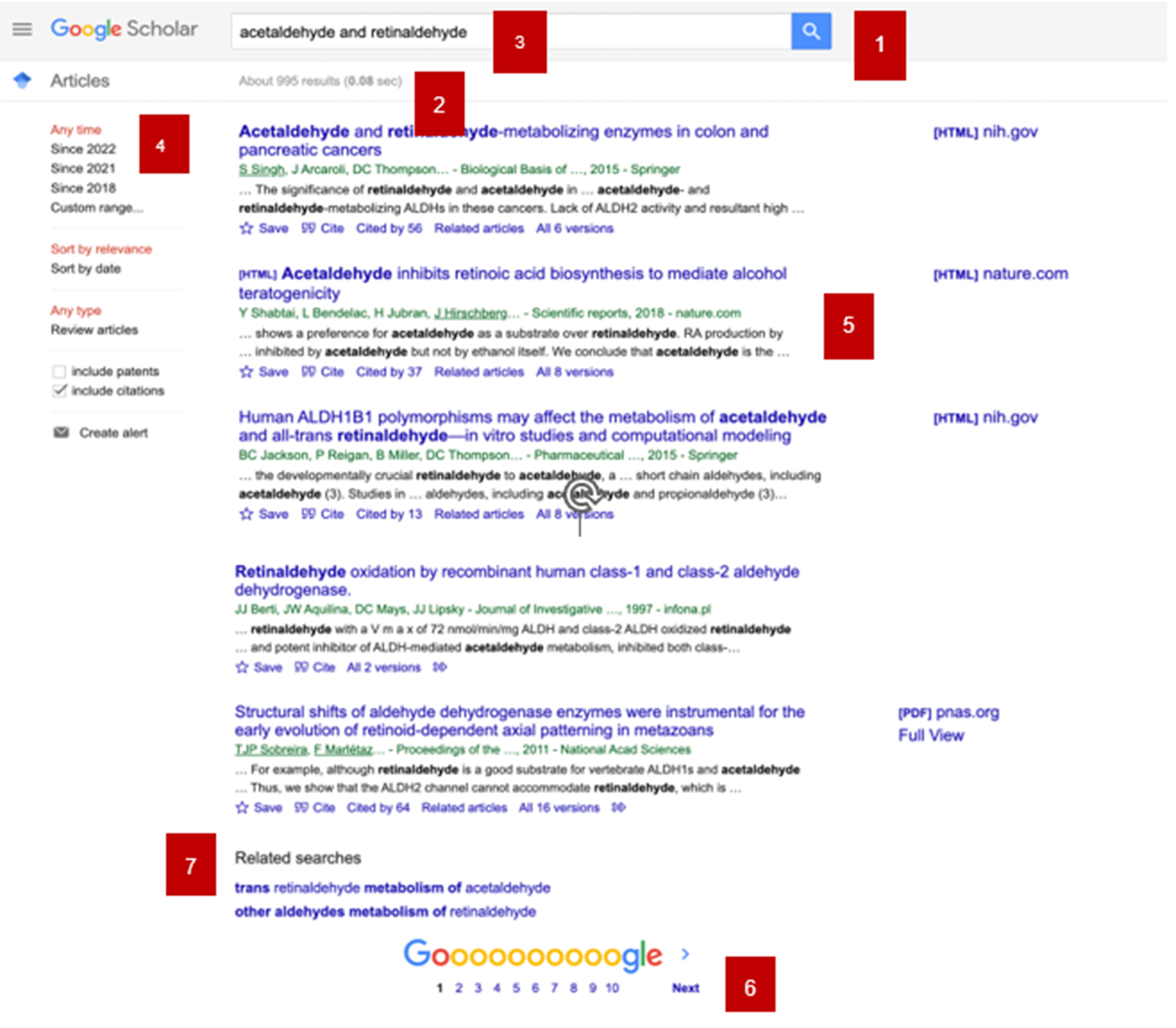
- New search
- The number of results from the search
- List of keywords selected for the search
- Area to reorder results
- Article results
- Change to another page of results
- Related searches
Refine search
Modify the time span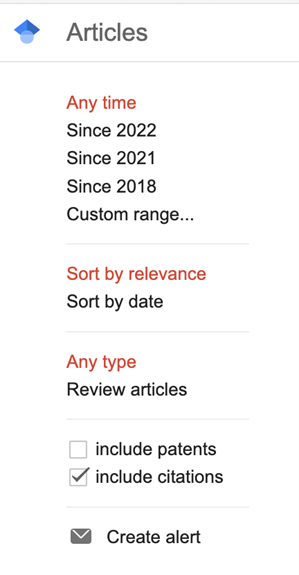
• In some cases, extending or reducing the time span of a search will provide more reviewers in that area of study and/or reviewers that are more responsive
• You can filter by 5 years or 10 years as well as a custom range by selecting from the filter options on the left side of the screen in the ‘Custom range’ category.
Sort by
- Sorting the search results by date will allow you to identify the most recent researchers in the field and who may be most relevant for reviewing new research
- On the Results page sort by ‘Sort by date’
Sort by Relevance
- Sorting by ‘Relevance’ will yield articles that are the closest match to your keyword search and may reveal researchers who have the greatest expertise in the field
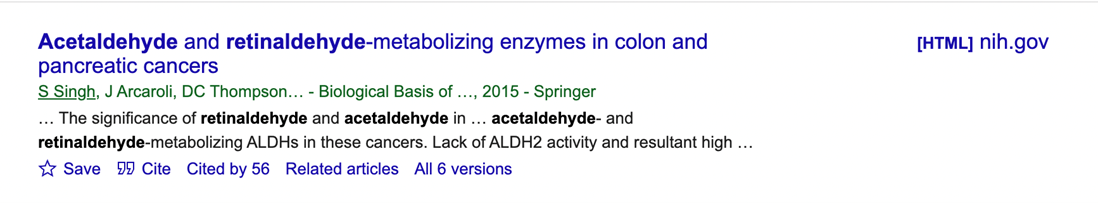
Viewing an article
To view an article, select the title from the Results page. Since Google Scholar is not a database as Web of Science or Scopus, how the articles look once you open them will depend on the journal they are published in.

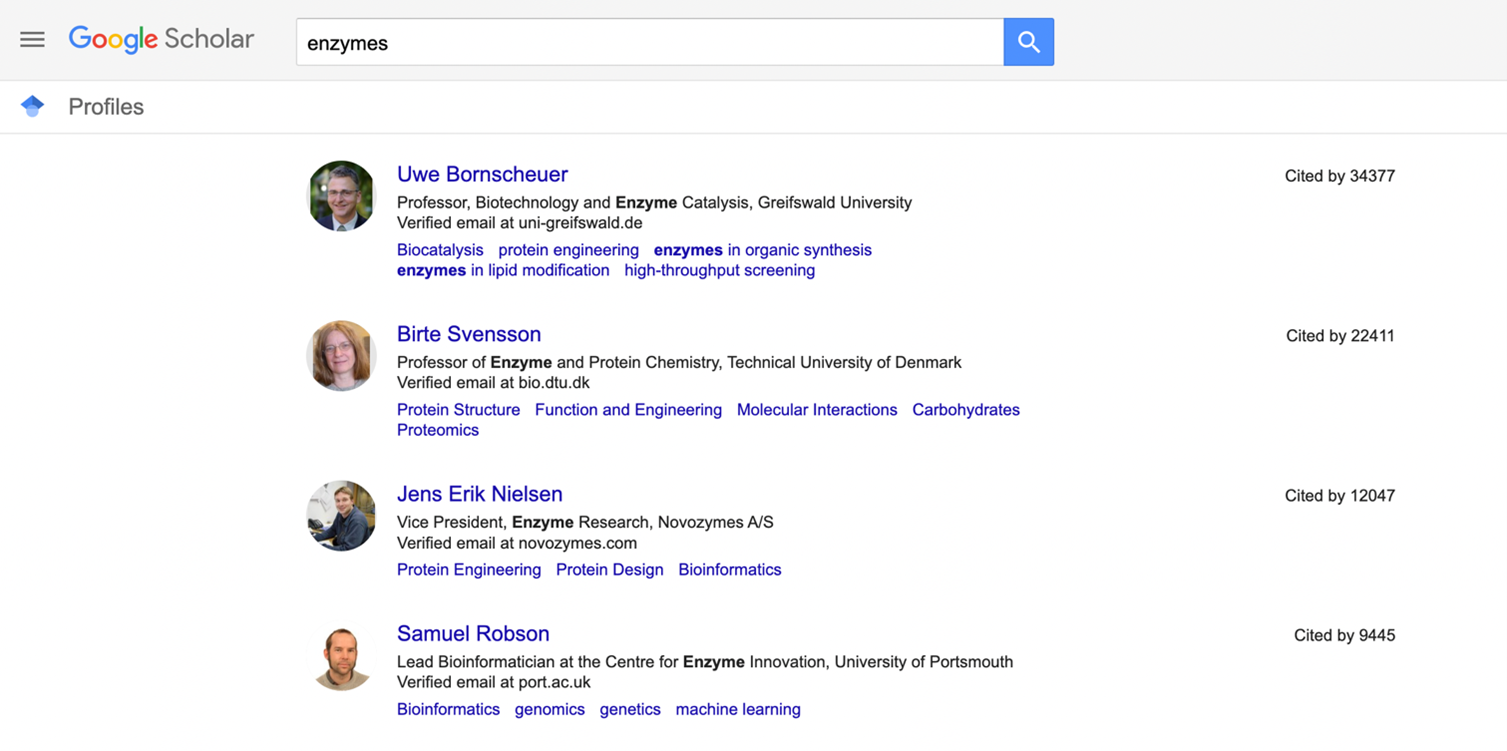
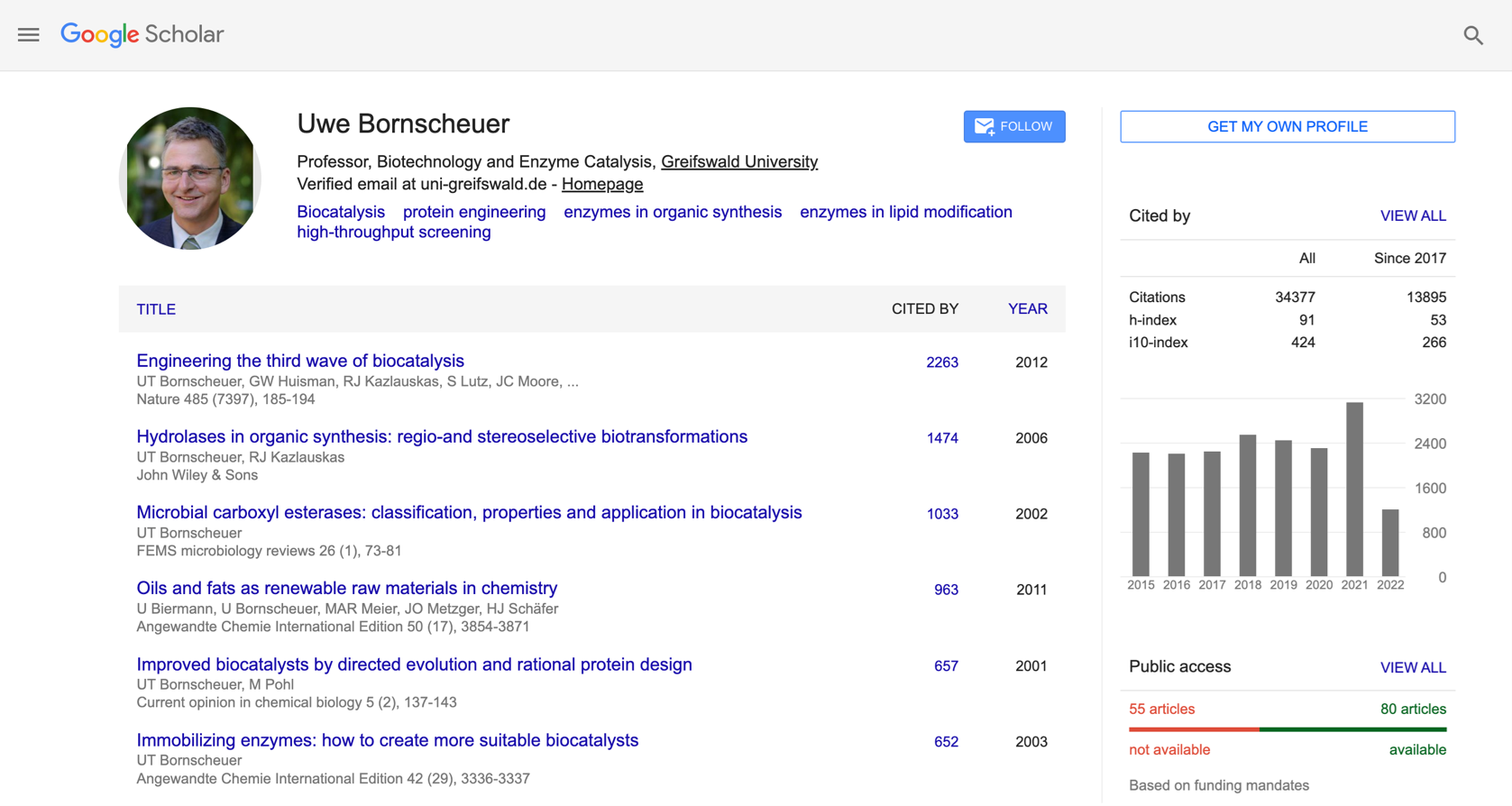
Researchers’ profiles 
This option allows you to search directly for researchers who have established that they work in the area of study of interest. The profiles manage labels that are added by the researchers so that they can be found more easily. The profiles are organized starting with the most cited and the rest of the profiles appear in decreasing order.
Search for profiles
There are two options to search for profiles. In the first one, you enter the keywords directly into the search bar. The results thus obtained will be broad because is not only limited to the words that are associated as labels, but also to words that are in the description of their occupation or the position they hold.
The second one is to write: ‘label:keyword’ or ‘label:keyword_keyword’ in case your keyword is a compound keyword. This search returns only the profiles that have these words as labels, it is more precise than the first one.
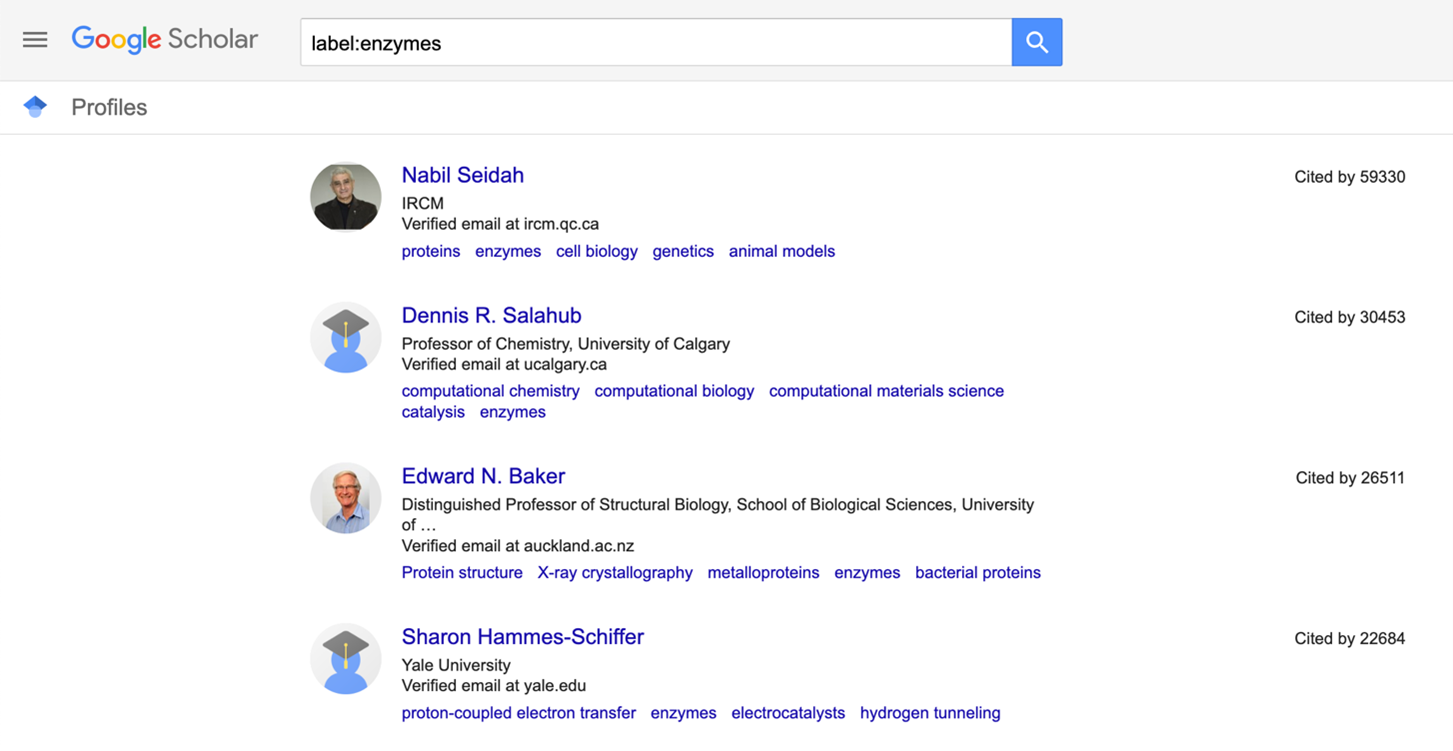
In addition, the vast majority of these profiles have listed the associated articles published by the researchers. These articles are organized in order of number of citations. These profiles also provide statistics on the authors, such as how many citations they have and indices such as the h-index and the i10-index. In many cases the search engine has verified the author's email address and provides the domain to which the email is associated
Reference list
- You can also find reviewers by searching for authors listed in the references
- Search online for the potential reviewer using the title of the referenced paper in order to ensure you identify the correct person.
NOTE
- Using the reference list for identifying potential reviewers should be a last resort
- Authors may have cited papers that are consistent with their own research and findings, so the reviewer’s assessment of the manuscript may be less objective
- It is also important to be particularly cautious of bias – the reviewer may look more favourably on a paper knowing that their own work will be cited if it is published.